¿Cómo logra el kit de catéter venoso central a través de la sinergia de varios componentes?
Análisis de los componentes centrales del kit
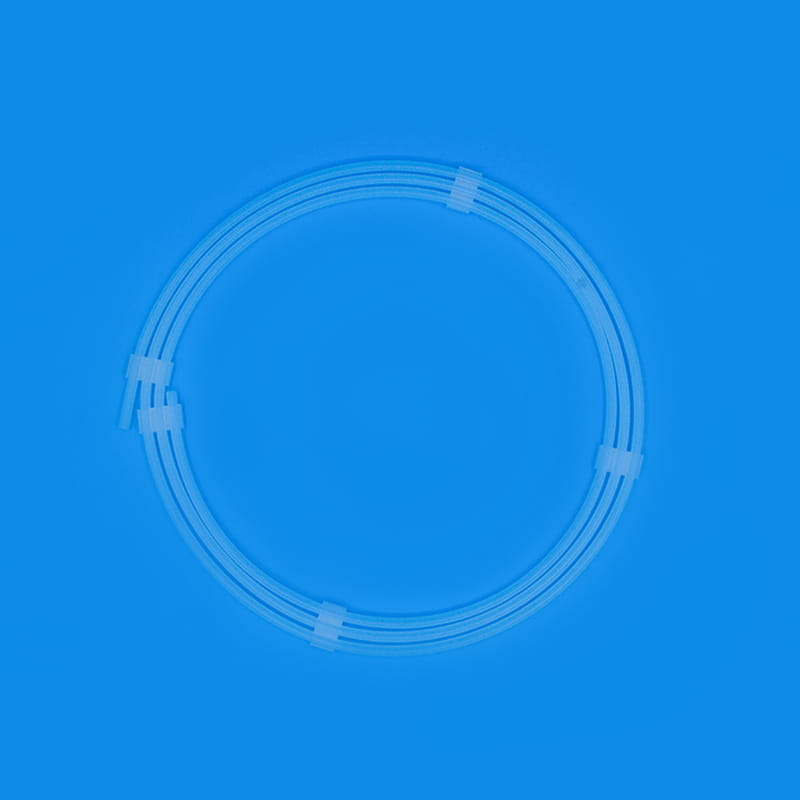
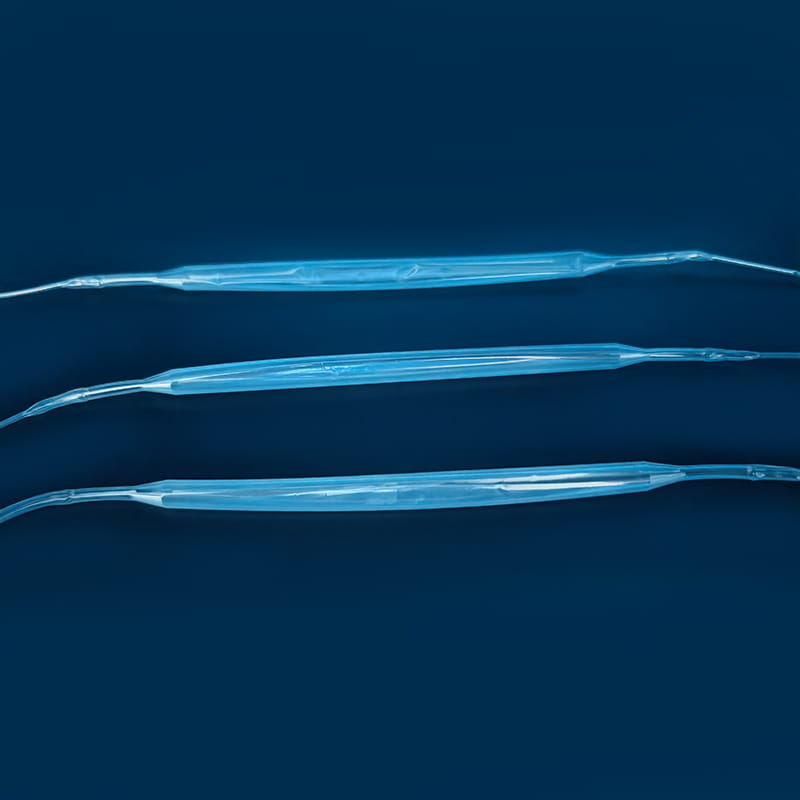
El Kit de catéter venoso central Contiene una variedad de componentes clave, cada uno de los cuales juega un papel único e insustituible en todo el proceso de operación médica. El primero es el catéter venoso central, que es el componente central del kit y es el canal que conecta la vena central fuera del cuerpo y dentro del cuerpo. Su material generalmente está hecho de poliuretano o silicona de grado médico. Dichos materiales tienen una buena biocompatibilidad y pueden reducir efectivamente el rechazo del cuerpo de los cuerpos extraños y reducir el riesgo de complicaciones como la infección. Los diferentes tipos de catéteres venosos centrales tienen sus propias características en estructura y función. Los catéteres de lumen individual son adecuados para las necesidades de tratamiento único, mientras que los catéteres de doble lumen o de múltiples lúmenes pueden realizar una variedad de operaciones médicas diferentes al mismo tiempo, como infusión, recolección de sangre y administración de medicamentos, lo que mejora en gran medida la eficiencia y la conveniencia de las operaciones médicas. En términos de diseño, algunas superficies de catéter se tratan con recubrimientos especiales para mejorar aún más las propiedades anti-trombóticas; Algunos también están marcados con escamas para facilitar el personal médico a comprender con precisión la profundidad de inserción.
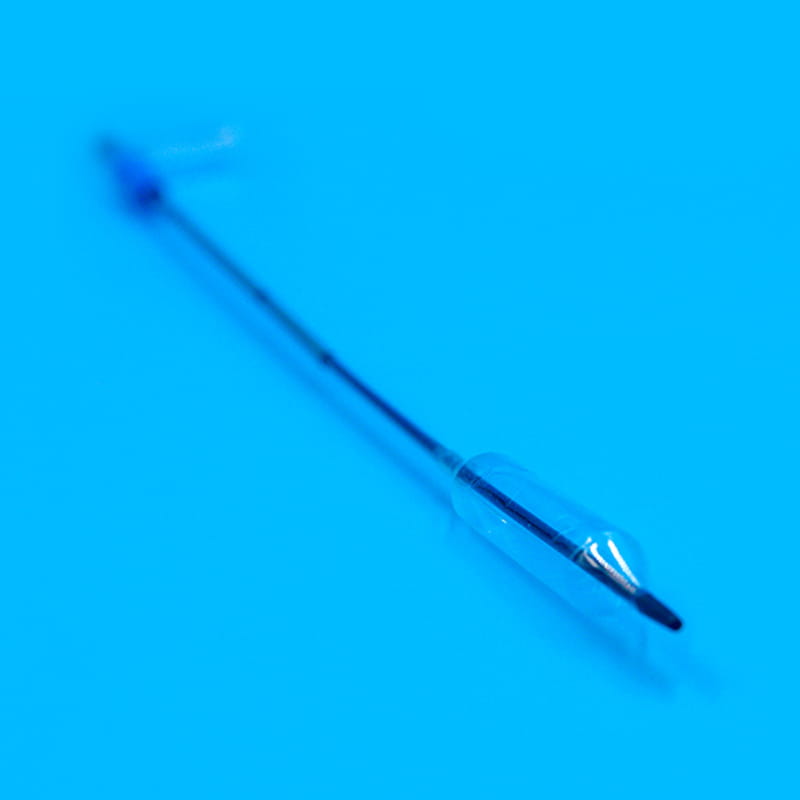
El cannula plays a pioneering role in the central venous catheter kit. When performing a central venous catheter insertion operation, the cannula is first used for percutaneous puncture into the vein. Its needle tip adopts a bevel cutting process. This design is sharp and precise, and can quickly and accurately penetrate the skin and vein wall with minimal resistance, opening a channel for the entry of subsequent components. The needle core and outer sleeve of the cannula needle are closely matched. When the cannula needle successfully enters the vein, the inner needle core is removed through a special separation mechanism, and the outer sleeve with a certain hardness and flexibility will remain in the vein as a guide channel for subsequent guide wires and other components to enter. To ensure the accuracy of puncture, some cannula needles are also equipped with ultrasound guidance adapters, which can be used with ultrasound equipment to observe the puncture path and blood vessel status in real time.
El guidewire is a key tool for precise positioning and guidance in the central venous catheter kit. After the cannula needle establishes the initial channel, the guidewire will be sent into the vein through the cannula. The outer layer of the guidewire is usually woven from medical-grade stainless steel wire, and the inner layer is a nickel-titanium alloy core. This structure gives the guidewire good flexibility and maneuverability. Doctors can use the J-shaped or straight head design of the guidewire tip to flexibly turn and guide it in the blood vessel through in vitro operation, and accurately send it to the target position. Some high-end guidewires also have a hydrophilic coating, which becomes lubricated after contact with blood, further reducing friction damage to the inner wall of the blood vessel. The existence of the guidewire makes the insertion path of the central venous catheter clearer and more controllable, laying a solid foundation for the smooth insertion of the subsequent catheter.
El role of the dilator in the central venous catheter kit should not be ignored. Since the diameter of the vein is relatively thin, and the central venous catheter needs to be smoothly inserted, it is necessary to properly dilate the vein. The dilator usually adopts a conical or cylindrical design, and the material is mostly medical-grade polyethylene. It can enter the vein along the guidewire and expand the channel of the venous puncture site by gradually expanding. During the expansion process, the smooth surface treatment and gradual caliber design of the dilator can reduce damage to the venous tissue while ensuring effective expansion. For special patients, such as those with thin blood vessel walls or sclerosis, there are also special controllable dilators available, and doctors can accurately adjust the expansion strength and range according to actual conditions.
El peelable sheath is an important part of the central venous catheter kit to ensure the safe insertion of the catheter. After the dilator completes the dilation of the vein, the peelable sheath will be sent into the vein along the guidewire and dilator. The peelable sheath consists of two symmetrical half sheaths connected by a special locking structure in the middle. When the peelable sheath reaches the appropriate position, the central venous catheter will be inserted into the vein through the sheath. At this time, the medical staff will separate the peelable sheath from the middle lock and remove it from the body through a specific operation technique, while the central venous catheter will be left in the vein. This unique design not only ensures the smooth catheter insertion process, but also avoids unnecessary damage to the vein and catheter. To prevent accidental scratches on the surrounding tissue when the sheath is peeled off, the edge of the sheath is specially rounded and blunted.
El fixing device plays a role in stabilizing and fixing the catheter in the central venous catheter kit. In order to ensure that the central venous catheter can maintain a stable position in the patient's body for a long time without displacement or falling off, fixing devices such as sutures, sterile dressings or special catheter fixers will be used to fix the catheter to the patient's skin. The suture fixation method is suitable for patients with long-term catheterization. The catheter is fixed to the skin tissue through delicate suturing operations; the sterile dressing is breathable, waterproof and antibacterial, and can effectively protect the puncture site; the dedicated catheter fixator is made of medical-grade silicone or polymer materials, and can be personalized according to the patient's skin morphology and catheter model through an adjustable buckle design. Appropriate fixation can not only ensure the normal function of the catheter, but also reduce the discomfort and potential risks caused to the patient by the movement of the catheter.
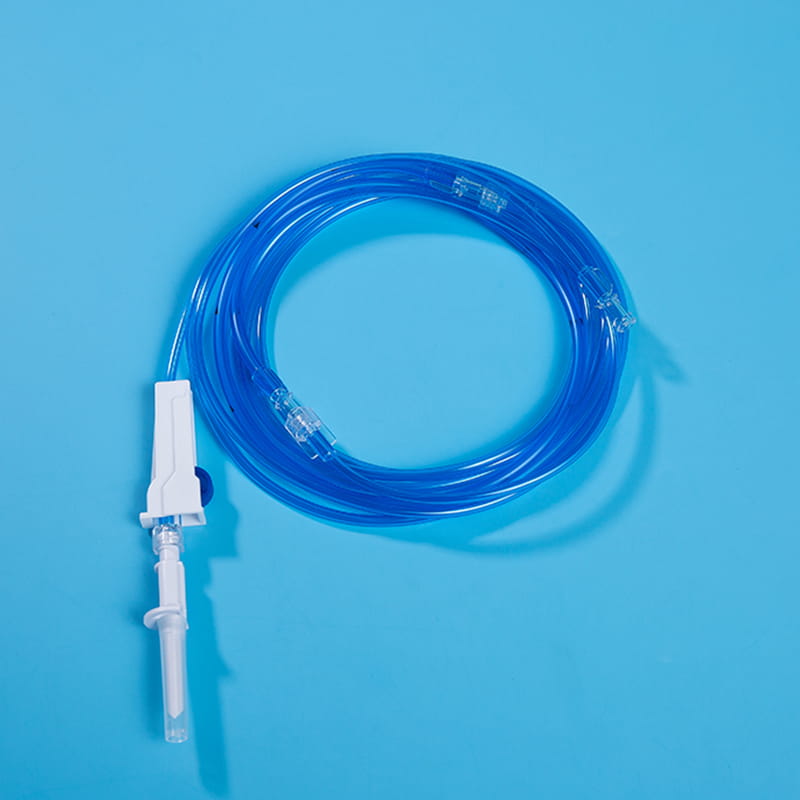
El interface for external connection is the bridge between the central venous catheter and external medical equipment. Through these interfaces, the central venous catheter can be connected to infusion sets, syringes and other equipment to achieve various medical operations such as infusion, drug administration, and blood collection. The design of these interfaces has good sealing and compatibility, and common ones include Luer connectors and needleless infusion connectors. The Luer connector is connected by threads to ensure a tight connection without leakage; the needleless infusion connector adopts a diaphragm design, which can complete the infusion operation without acupuncture, reducing the risk of infection. At the same time, some interfaces also have anti-backflow function to prevent blood from reflux and blocking the catheter, and support multiple devices to be connected at the same time to meet complex clinical needs.
Amplia gama de escenarios de aplicación clínica
En aplicaciones médicas reales, los escenarios de uso de los kits de catéteres venosos centrales son muy amplios. En el campo de la atención intensiva, para pacientes con condiciones críticas que necesitan una gran cantidad de infusión y medicamentos frecuentes, los catéteres venosos centrales pueden proporcionar un canal de infusión rápido y estable para satisfacer las necesidades de los pacientes y los medicamentos. Tomando a los pacientes con shock séptico como ejemplo, durante el proceso de rescate, una gran cantidad de líquido cristaloide, líquido coloide y fármacos vasoactivos deben complementarse en un corto período de tiempo. El catéter venoso central puede garantizar que estos fluidos y medicamentos ingresen rápidamente a la circulación sanguínea y corregir rápidamente el estado de choque. Al mismo tiempo, el monitoreo hemodinámico también se puede realizar a través del catéter venoso central. El médico conecta el sensor de presión a la interfaz del catéter para obtener parámetros, como la presión venosa central y la presión de cuña de la arteria pulmonar en tiempo real, lo que ayuda a los médicos a comprender la función cardíaca del paciente y el estado de circulación sanguínea en tiempo real, y proporciona una base importante para formular planes de tratamiento precisos.
En el tratamiento tumoral, muchos medicamentos de quimioterapia son altamente irritantes para los vasos sanguíneos, y la administración a través de las venas periféricas puede causar complicaciones como la flebitis. El kit de catéter venoso central puede colocar un catéter en la vena central, permitiendo que los medicamentos de quimioterapia ingresen directamente a los vasos sanguíneos grandes y se diluyan rápidamente, reduciendo así la irritación a los vasos sanguíneos, reduciendo la probabilidad de complicaciones y mejorando la tolerancia y el cumplimiento del tratamiento de los pacientes. Por ejemplo, los pacientes con cáncer de mama que reciben medicamentos de quimioterapia altamente irritantes como la doxorrubicina pueden usar catéteres venosos centrales para evitar consecuencias graves como la necrosis de la piel y la ulceración tisular causada por la extravasación de los fármacos. Al mismo tiempo, para los pacientes que necesitan quimioterapia a largo plazo y múltiples, los catéteres venosos centrales reducen el dolor de las puntas repetidas y mejoran la continuidad del tratamiento.
Además, en la terapia de apoyo nutricional, los catéteres venosos centrales pueden usarse para el apoyo nutricional parenteral total para pacientes que no pueden tomar suficiente nutrición a través del tracto gastrointestinal, como pacientes con coma a largo plazo y quemaduras graves. Dar una solución de nutrientes de alta concentración de alta concentración a través de la vena central puede satisfacer las necesidades de nutrientes del cuerpo del paciente y promover la recuperación del paciente. Tomando a los pacientes con quemaduras extensas como ejemplo, su función gastrointestinal se suprime debido al trauma, y no pueden digerir y absorber los alimentos normalmente. En este momento, la solución de nutrientes todo en uno que contiene aminoácidos, emulsión de grasas, glucosa y otros ingredientes se administra a través del catéter venoso central para mantener el equilibrio de nitrógeno del paciente, repone la energía requerida por el cuerpo y acelera la cicatrización de la herida. Al mismo tiempo, el personal médico también puede monitorear los electrolitos del paciente, el azúcar en la sangre y otros indicadores a través del catéter venoso central y ajustar el plan de apoyo nutricional a tiempo.
Procedimientos operativos estrictos y estandarizados
El operating procedures of the central venous catheter kit need to strictly follow the specifications and standards. Before the operation, the doctor needs to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the patient's condition, including the patient's age, weight, underlying diseases, coagulation function, etc., and select the appropriate puncture site and central venous catheter type. Common puncture sites include the internal jugular vein, subclavian vein and femoral vein. Different sites have their own advantages and disadvantages, and they need to be carefully selected according to the specific situation of the patient. At the same time, detailed explanations and communication should be given to the patient, and the patient should be informed of the operation process, possible risks and key points of cooperation to obtain the patient's cooperation. During the operation, the principle of aseptic operation must be strictly followed. The puncture site must be disinfected with iodine more than three times, and the diameter of the disinfection range must not be less than 15 cm. A large sterile sheet must be laid to ensure that the entire operation is carried out in a sterile environment. Then follow the steps of trocar puncture, guide wire insertion, dilation with a dilator, insertion of a removable sheath, insertion of a central venous catheter, fixation of the catheter, and connection of an external interface. Taking internal jugular vein puncture as an example, under ultrasound guidance, after determining the puncture point, the trocar is inserted at an angle of 30-45 degrees. After seeing the blood return, it is confirmed that it is in the vein, and then the subsequent components are inserted according to the process. After the operation is completed, the patient needs to be closely observed and cared for, and the patient must be monitored for complications and treated in a timely manner. This includes observing whether the puncture site is red, swollen, or exuded, and changing the dressing regularly; monitoring the patient's body temperature, blood routine, and other indicators to determine whether an infection has occurred; evaluating the function of the catheter to ensure smooth infusion, blood collection, and other operations.
Desafíos y riesgos enfrentados
Aunque los kits de catéter venoso central juegan un papel importante en el campo de la medicina, también enfrentan algunos desafíos y riesgos durante el uso. La infección es una de las complicaciones más comunes de los catéteres venosos centrales. Dado que el catéter queda en el cuerpo durante mucho tiempo, es fácil que las bacterias y otros microorganismos invadan, causando infección local o infección sistémica. Las bacterias ingresan principalmente al cuerpo a través de la colonización de la piel en el sitio de punción, la contaminación del conector del catéter y la contaminación del sistema de infusión. La trombosis también es un problema que no se puede ignorar. El catéter puede estimular el endotelio vascular en el vaso sanguíneo, causando cambios en la coagulación de la sangre, formando así un trombo. Una vez que el trombo se cae, puede causar complicaciones graves como la embolia pulmonar. Además, problemas como el bloqueo y el desplazamiento del catéter también pueden afectar el uso normal y el efecto del tratamiento del catéter venoso central. El bloqueo del catéter puede ser causado por la deposición de drogas, la coagulación de la sangre, etc.; El desplazamiento del catéter puede estar relacionado con factores como la actividad inadecuada del paciente y la fijación suelta.
For more information, please call us at +86-18913710126 or email us at .
Los procedimientos de intervención vascular son parte integral de la medicina cardiovascular mode...
Introducción Tubo endobronquial de una sola luz Los s son un componen...
En la medicina moderna, los catéteres médicos son herramientas indispensables que se utilizan en ...
En la industria de la salud, no se puede subestimar la importancia de seleccionar los materiales ...
En la era de la medicina de precisión, un pequeño tubo a menudo lleva el peso de las responsabili...
En la atención sanitaria moderna, la gestión precisa de los líquidos es crucial para la seguridad...